Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
赤松 憲
no journal, ,
新しく開発したDNA損傷スペクトル分析法とその適用例について紹介する。この方法では、DNA分解酵素として、DNAの構成要素であるヌクレオチドを、DNA末端から逐次切り出す蛇毒ホスホジエステラーゼ(SVPD)、及びウシ腸アルカリホスファターゼ(CIAP)を用いる。SVPDの基質特異性(リン酸が残っているDNA末端は認識しない)とそのミカエリス・メンテン型の反応速度論的性質(反応初期において、DNA末端量と切り出されたヌクレオチド量は比例関係にある)により、鎖切断末端のリン酸基の有無,ピペリジン脆弱性部位(電子吸引性の損傷塩基及び脱塩基部位)というカテゴリーで損傷を分類することが可能である。本方法で分析したDNA損傷スペクトルが線源間でどのように違うかを紹介し、他の情報と合わせながら議論したい。
藤井 健太郎; 横谷 明徳; 鹿園 直哉
no journal, ,
軟X線照射によって乾燥DNA中に生じる分子主鎖切断及び酸化的塩基損傷の収率をアガロース電気泳動法により検出した。塩基損傷の検出は、照射試料を塩基除去修復酵素で処理することによって塩基損傷を鎖切断に変換することで定量化した。それぞれの収率は、軟X線のエネルギーに依存し、特に酸素K殻吸収によって鎖切断及び塩基損傷の収率の有意な増加が見られた。講演ではこれらのDNA損傷の生成機構について議論する。
渡辺 立子; 佐藤 理*; 久保田 あさ子*; 船曳 淳*; 斎藤 公明
no journal, ,
本研究の目的は、われわれが新たに構築したシステムを用いて、重粒子線によるエネルギー付与の微細構造がDNA損傷の初期生成スペクトル(損傷数及びDNA上の損傷の位置関係)にどのように反映され、また、飛跡内でどのようにDNA損傷が分布するかを推測し、LET及びイオン核種による生物効果の違いとの関連性を探ることである。本発表では、細胞環境,水溶液のDNAサンプルを想定した条件下で、ヘリウム,炭素,ネオン,鉄イオンについて計算したDNA損傷スペクトルのLET依存性を示すとともに、一部のイオンについては飛跡に沿った損傷分布についてのデータを示す。
勝村 庸介; 山下 真一; Lin, M.; 室屋 裕佐*; Meesungnoen, J.*; Jay-Gerin, J.-P.*; 村上 健*
no journal, ,
Understanding of water radiolysis with low LET radiations as well as with high LET ones is essential to clarify radiation damage to DNA. Measurements of water decomposition yields have been determined with highly energetic heavy-ion beams at HIMAC in the National Institute of Radiological Sciences. In parallel to the measurements, Monte-Carlo simulations have also been performed. Finally, characteristics of intra-track reactions induced by heavy ion beams were discussed in terms of the spatial track structure and LET dependence of radiation-induced biological phenomena.
野口 実穂; 漆原 あゆみ*; 横谷 明徳; O'Neill, P.*; 鹿園 直哉
no journal, ,
電離放射線は放射線の飛跡に沿って電離や励起を起こし、DNAにさまざまな損傷を生じる。放射線のDNA損傷で特徴的なのは電離や励起や密に起こることで生じるクラスターDNA損傷である。クラスター損傷はDNAの1 2ヘリカルターンに2個以上の損傷を持つものとして定義されている。生じるクラスター損傷は理論的には一本鎖切断(SSB)に塩基損傷を伴ったような損傷が多いと言われている。in vitroではSSBと塩基損傷8-oxoGが近傍にあると、SSBが8-oxoGの変異を増強することが報告されている。これを踏まえて、本研究では人工的に合成したモデルクラスター損傷を用いて突然変異誘発を調べる細胞内実験系を利用し、細胞内(大腸菌内)でSSBが8-oxoGの変異にどのような影響をあたえるかを検討した。8-oxoGと相補鎖のSSBとによるクラスター損傷の場合、8-oxoG単独の損傷よりも突然変異誘発率が上昇した。特にMutY欠損株の結果からSSBが8-oxoGの除去を阻害していることが示唆された。しかし、8-oxoGとSSBとが同一鎖上にあるクラスター損傷では8-oxoG単独で高い変異率を示したfpg, mutY株でも突然変異誘発率の上昇は全く認められなかった。以上から8-oxoGと相補鎖のSSBの場合、相補鎖のSSBが8-oxoGの修復を阻害すること、同一鎖の場合、8-oxoGはSSBの修復に伴い除去されている可能性がある、ことが考えられ、8-oxoGとSSBとのクラスター損傷ではSSBが二本鎖のどちらに存在するかにより突然変異誘発率が大きく変化することが推測された。
2ヘリカルターンに2個以上の損傷を持つものとして定義されている。生じるクラスター損傷は理論的には一本鎖切断(SSB)に塩基損傷を伴ったような損傷が多いと言われている。in vitroではSSBと塩基損傷8-oxoGが近傍にあると、SSBが8-oxoGの変異を増強することが報告されている。これを踏まえて、本研究では人工的に合成したモデルクラスター損傷を用いて突然変異誘発を調べる細胞内実験系を利用し、細胞内(大腸菌内)でSSBが8-oxoGの変異にどのような影響をあたえるかを検討した。8-oxoGと相補鎖のSSBとによるクラスター損傷の場合、8-oxoG単独の損傷よりも突然変異誘発率が上昇した。特にMutY欠損株の結果からSSBが8-oxoGの除去を阻害していることが示唆された。しかし、8-oxoGとSSBとが同一鎖上にあるクラスター損傷では8-oxoG単独で高い変異率を示したfpg, mutY株でも突然変異誘発率の上昇は全く認められなかった。以上から8-oxoGと相補鎖のSSBの場合、相補鎖のSSBが8-oxoGの修復を阻害すること、同一鎖の場合、8-oxoGはSSBの修復に伴い除去されている可能性がある、ことが考えられ、8-oxoGとSSBとのクラスター損傷ではSSBが二本鎖のどちらに存在するかにより突然変異誘発率が大きく変化することが推測された。

鹿園 直哉; Pearson, P.*; Thacker, J.*; O'Neill, P.*
no journal, ,
ジヒドロチミンと8-オキソグアニンと呼ばれる塩基損傷からなるクラスター損傷のプロセシングに関する知見を得る目的から、大腸菌の野生株において、塩基損傷が除去された後生ずると考えられる修復中間体の形質転換効率及び変異誘発頻度を調べた。その結果、「ジヒドロチミンと脱塩基部位」もしくは「ジヒドロチミンと鎖切断」では変異頻度が高くないが、塩基損傷のない「脱塩基部位と脱塩基部位」もしくは「脱塩基部位と鎖切断」ではともに、形質転換効率は非常に低くかつ変異頻度は非常に高いことがわかった。これらの結果から、8-オキソグアニンもしくはジヒドロチミンのどちらかが除去された後に残ったクラスター損傷内の塩基損傷は、脱塩基部位や鎖切断には変換されないことが示唆された。
浜田 信行*; Ni, M.; 金杉 勇一*; 岩川 眞由美*; 今留 香織*; 舟山 知夫; 坂下 哲哉; 楚良 桜*; 今井 高志*; 高倉 かほる*; et al.
no journal, ,
Here we have investigated heavy ion-induced bystander response in confluent human fibroblast cultures. First, precise microbeams were employed to target 0.0003% of cells. Conventional broadfield irradiation was carried out in parallel to see the effects in irradiated cells. Intriguingly, bystander cells manifested a more transient apoptotic response and delayed p53 phosphorylation, compared with irradiated cells. Taken together, nearly three quarters of the genes whose expression changed in bystander cells were downregulated, and most of the genes upregulated in irradiated cells were downregulated in bystander cells. These findings highlight the distinct response of irradiated and bystander cells. Furthermore, interleukin genes were upregulated in irradiated cells whereas its receptor gene was upregulated in bystander cells, suggestive of the signal transmission from irradiated to bystander cells. Second, chromosome aberrations were analyzed in cells treated with conditioned medium from X- or heavy ion-irradiated cells. We found the difference in the types of aberrations, but very little in the total aberration yields, indicating that bystander responses occur independently of radiation types but are induced through different mechanisms. Collectively, these induced bystander responses could be a defensive mechanism that would avert or minimize further expansion of aberrant cells.
松本 英樹*; 冨田 雅典*; 大塚 健介*; 舟山 知夫; 小林 泰彦
no journal, ,
The radioadaptive response, radiation-induced bystander responses, low-dose radio-hypersensitivity, and genomic instability are specifically observed in response to low dose/low dose-rate radiation, and the mechanisms underlying these responses often involve biochemical/molecular signals that respond to targeted and non-targeted events. However, mechanisms of these phenomena are not fully known. To elucidate the mechanisms of radiation-induced bystander responses, we analyzed the formation of  H2AX and pNBS1 foci after irradiation of a targeted cell with 460 MeV
H2AX and pNBS1 foci after irradiation of a targeted cell with 460 MeV  Ar microbeams. We found that the foci of
Ar microbeams. We found that the foci of  H2AX and pNBS1 were formed in the unirradiated cells in the colony including the targeted cell 6 h after the irradiation and that this formation of these foci was almost completely suppressed by the addition of DMSO or Lindane. Also we found that the foci of
H2AX and pNBS1 were formed in the unirradiated cells in the colony including the targeted cell 6 h after the irradiation and that this formation of these foci was almost completely suppressed by the addition of DMSO or Lindane. Also we found that the foci of  H2AX and pNBS1 were formed in the unirradiated cells in the colonies not including the targeted cell 6 h after irradiation and that this formation of the foci was almost completely suppressed by the addition of aminoguanidine or c-PTIO. Our findings strongly suggested that ROS and NO may be actually initiators/mediators for evoking radiation-induced bystander responses.
H2AX and pNBS1 were formed in the unirradiated cells in the colonies not including the targeted cell 6 h after irradiation and that this formation of the foci was almost completely suppressed by the addition of aminoguanidine or c-PTIO. Our findings strongly suggested that ROS and NO may be actually initiators/mediators for evoking radiation-induced bystander responses.
坂本 綾子; 中川 繭; 高橋 真哉*; 清水 喜久雄*; 田中 淳; 鳴海 一成
no journal, ,
To survive under the challenging circumstances, plants equip themselves with damage tolerance mechanisms, such as translesion synthesis (TLS). During our attempt to isolate novel genes accounting for the UV-resistance, we found several genes that seem to be involved in TLS. These are 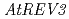 ,
, 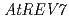 ,
, 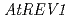 and
and 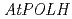 . All these disruptants were more sensitive to UV exposure than wild-type plant although the levels of sensitivity were different each other. To obtain further information about plant TLS mechanisms, we analyzed bacterially expressed AtREV1 protein
. All these disruptants were more sensitive to UV exposure than wild-type plant although the levels of sensitivity were different each other. To obtain further information about plant TLS mechanisms, we analyzed bacterially expressed AtREV1 protein  . The recombinant AtREV1 protein inserted a dCMP at the opposite of AP site, but never inserted a nucleotide opposite of CPD nor 6-4 photoproducts. We also measured the UV-induced mutation frequencies in
. The recombinant AtREV1 protein inserted a dCMP at the opposite of AP site, but never inserted a nucleotide opposite of CPD nor 6-4 photoproducts. We also measured the UV-induced mutation frequencies in 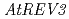 -,
-, 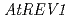 - or
- or 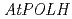 -disrupted plants. The disruption of
-disrupted plants. The disruption of 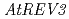 or
or 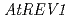 reduced the reversion frequency to 1/4 of the level of wild type, while the disruption of
reduced the reversion frequency to 1/4 of the level of wild type, while the disruption of 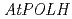 enhanced the frequency more than twice. These results suggest that UV-induced damage is processed by two competitive pathways in Arabidopsis: a more mutagenic pathway with AtREV3 and AtREV1 and a less mutagenic pathway with AtPOLH.
enhanced the frequency more than twice. These results suggest that UV-induced damage is processed by two competitive pathways in Arabidopsis: a more mutagenic pathway with AtREV3 and AtREV1 and a less mutagenic pathway with AtPOLH.
横谷 明徳; 鹿園 直哉; 漆原 あゆみ*; 藤井 健太郎
no journal, ,
放射線により誘発されるクラスターDNA損傷内の多重1本鎖切断を観測するため、DNA変性を利用した新しい定量法を開発した。本方法では、放射線照射されたDNAは1本鎖DNAに変性処理した後に分析される。多重1本鎖切断がDNA2重鎖の両鎖に分布し、かつ2本鎖切断に至らない場合には、アガロースゲル上の正常1本鎖DNAのバンド強度の、線量に依存した減少量を観測することで切断頻度が得られる。熱的処理による付加的なheat labile損傷を避けるため、変性処理は50%のフォルムアミドを加え37 Cで行った。DNAの希薄溶液にX線を照射し1本鎖切断のほとんどがOHラジカルで生じる条件下で本実験系をテストしたところ、理論的に予測されるように閉環構造の線量効果曲線を利用するこれまでの手法で得られた線量効果曲線のちょうど1/2の傾きの1本鎖DNAの線量効果曲線が得られた。これにより、本方法の変性処理に起因するartifactによるDNA損傷は生じていないことが確認できたため、他の高LET放射線にもこの手法が適用できる見通しを得た。
Cで行った。DNAの希薄溶液にX線を照射し1本鎖切断のほとんどがOHラジカルで生じる条件下で本実験系をテストしたところ、理論的に予測されるように閉環構造の線量効果曲線を利用するこれまでの手法で得られた線量効果曲線のちょうど1/2の傾きの1本鎖DNAの線量効果曲線が得られた。これにより、本方法の変性処理に起因するartifactによるDNA損傷は生じていないことが確認できたため、他の高LET放射線にもこの手法が適用できる見通しを得た。
鵜飼 正敏*; 横谷 明徳; 野中 裕介*; 藤井 健太郎; 斎藤 祐児
no journal, ,
電子的な特性の観点からDNAの水和構造を明らかにするため、DNAが溶解した液体試料を液体分子線として真空中に導出した後これに対する光電子分光実験が可能となる装置を開発した。光源として、シンクロトロン軟X線を分光して得たビームを用いた。本発表では、(1)AMP, CMP及びGMPの各ヌクレオチド分子の水溶液に対する窒素K吸収端領域における全電子収量スペクトルを測定した結果を発表する。このスペクトルは吸収スペクトルに対応する。また、(2)水の部分光電子断面積を酸素K吸収端付近で測定した。実験はSPring-8の軟X線ビームライン(BL23SU)で行った。試料液体分子線は真空中で =20
=20 m程度であり、これに直交するように50
m程度であり、これに直交するように50 m程度まで集光した単色軟X線ビームを照射した。
m程度まで集光した単色軟X線ビームを照射した。